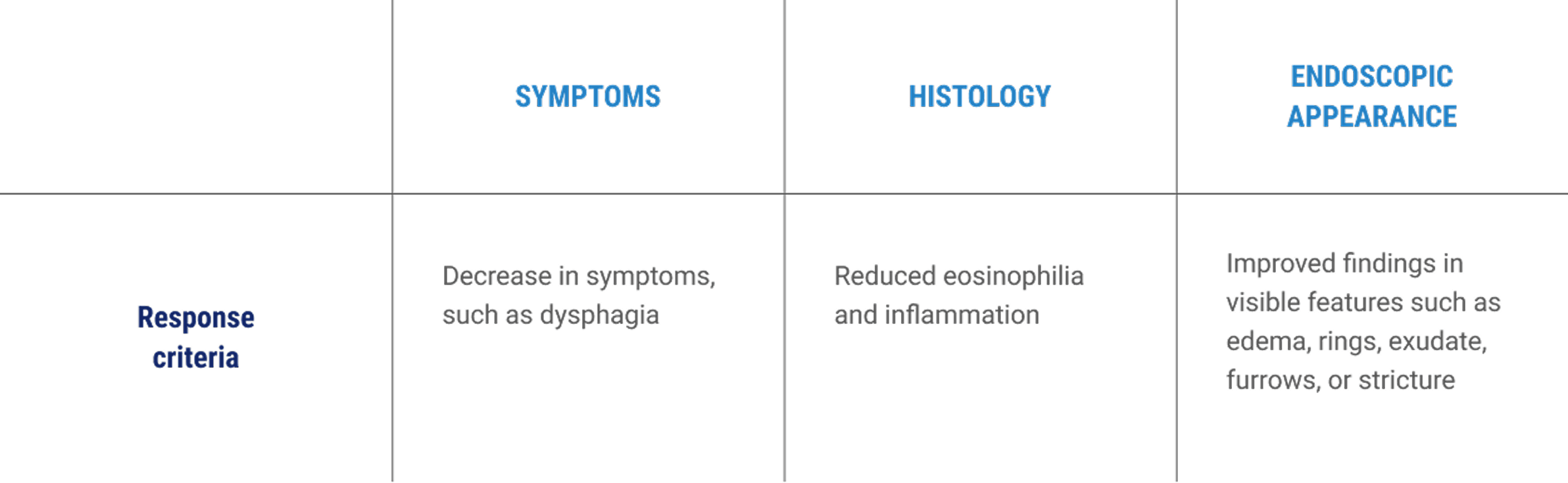
EoE REQUIRES A LONG-TERM MANAGEMENT APPROACH THAT FOCUSES ON 3 KEY AREAS: SYMPTOMS, HISTOLOGY, ENDOSCOPIC APPEARANCE1
Symptoms are one part of diagnosing and monitoring EoE, and can vary between patients and across age groups2
 Children
Children
(≤11 years)
-
Regurgitation
- Vomiting
- Food refusal
- Abdominal pain
- Failure to thrive
 Adult and
Adult and
adolescent
(≥12
years)
-
Dysphagia
-
Food impaction
-
Nonswallowing chest pain
-
Heartburn
-
Regurgitation
Symptoms often progress from feeding difficulties in young children to dysphagia and food impaction in adolescents and adults.
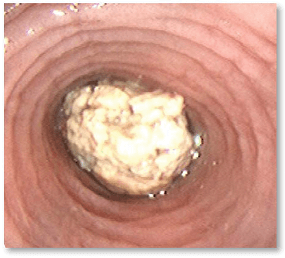
As EoE progresses, dysphagia can worsen, and food impactions may require ER visits3
The ACG and ASGE recommend a biopsy at the time of food impaction removal to help confirm EoE diagnosis as early as possible.1,4
Studies show that approximately 54% of patients who had esophageal biopsies collected at the time of food impaction removal had EoE5,6
Even in the absence of symptoms, the underlying type 2 inflammation can still be present7
Symptoms don’t always correlate with histology.
If the disease and underlying inflammation is not monitored, patients are at risk of undetected disease progression.

Adaptive behaviors can mask EoE symptoms and delay diagnosis, management, and disease surveillance8,9
Most people with EoE develop adaptive behaviors (coping mechanisms) to help manage their symptoms and avoid food impactions.10
Adaptive behaviors can contribute to a delay in EoE diagnosis that can increase the risk of severe disease complications.3,8


Consider asking your patients and caregivers questions to uncover these common adaptive behaviors11
mbibe fluids with meals
odify foods (cut into small pieces/puree)
rolong meal times
void hard texture foods
hew excessively
urn away tablets/pills
Children may exhibit different types of adaptive behaviors than adult patients11
-
Refusing food and pocketing food in their cheek
-
Difficulty advancing from pureed to solid food
-
Have trouble expanding their diet to include new flavors and textures
ACG, American College of Gastroenterology; ASGE, American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.

It’s important to look beyond symptoms and address persistent inflammation,
which can cause structural changes to the esophagus7

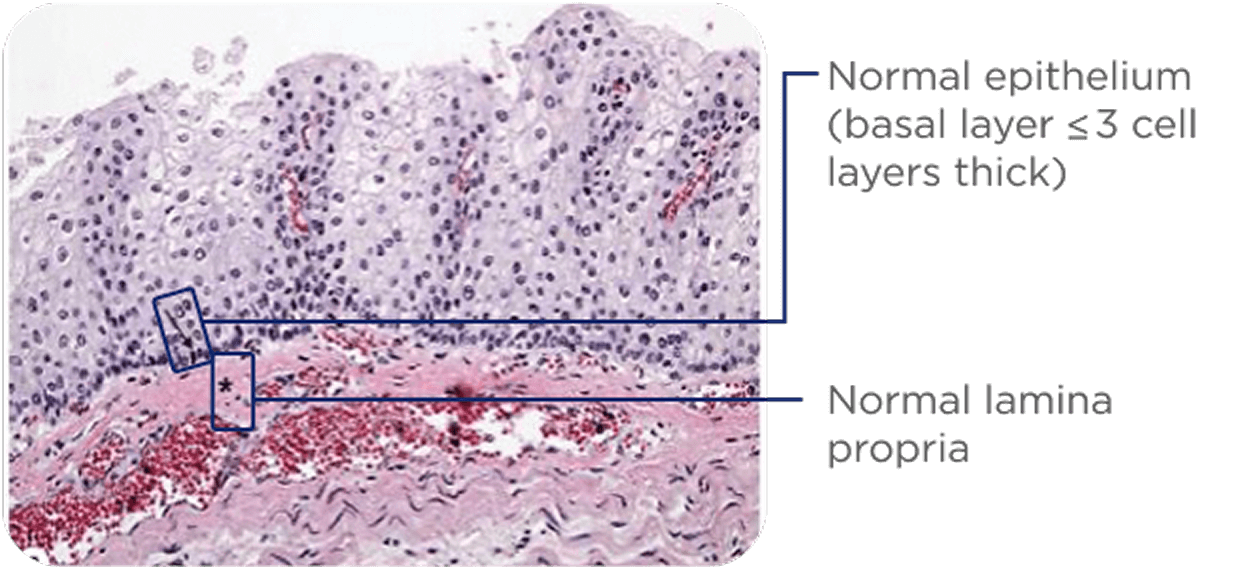
Histology can reveal eosinophilic infiltrate as well as other abnormalities1
Esophageal eosinophil counts are used to establish a diagnosis of EoE and are commonly used to assess treatment outcomes: ≥15 EOS/HPF required for diagnosis of EoE.1,12,13
Due to the patchiness of the disease, the ACG and ASGE recommend taking ≥6 biopsy samples from two distinct esophageal levels (proximal/mid, distal) to diagnose EoE.1,4
Biopsy Sensitivity for EoE Diagnosis in Adult Patients (N=66)14,a
aUsing a criterion of ≥15 EOS/HPF.
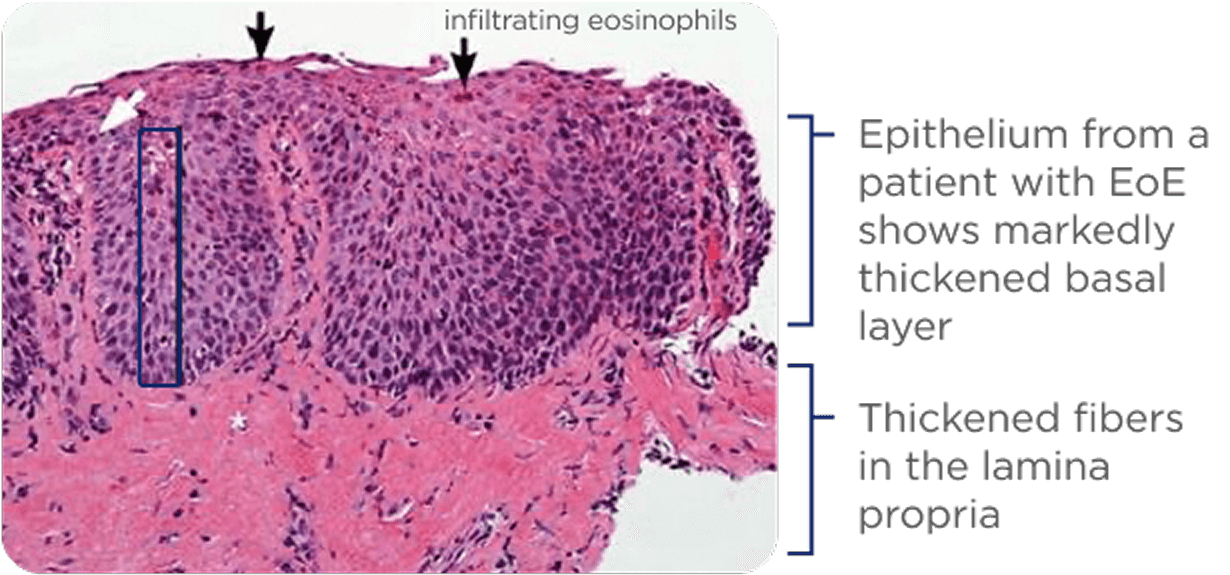
Histology can be used to reveal tissue abnormalities driven by inflammatory cells and mediators other than eosinophils.1
Healthy tissue4
Select EoE tissue abnormalities, indicative of fibrosis15
The ACG guidelines and ASGE consensus guidance recommend evaluating
endoscopic appearance and histology, and not symptoms alone,
to assess EoE activity during treatment1,4
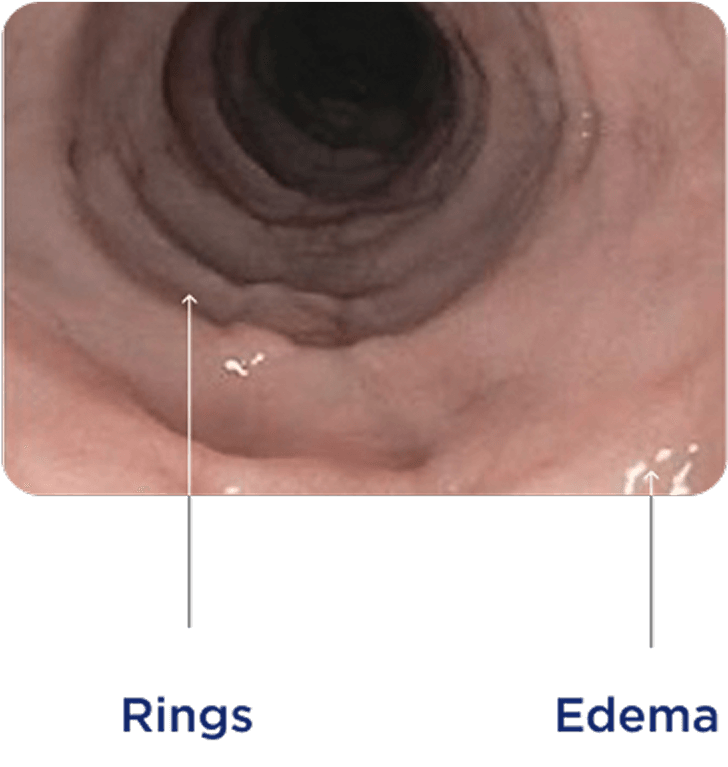
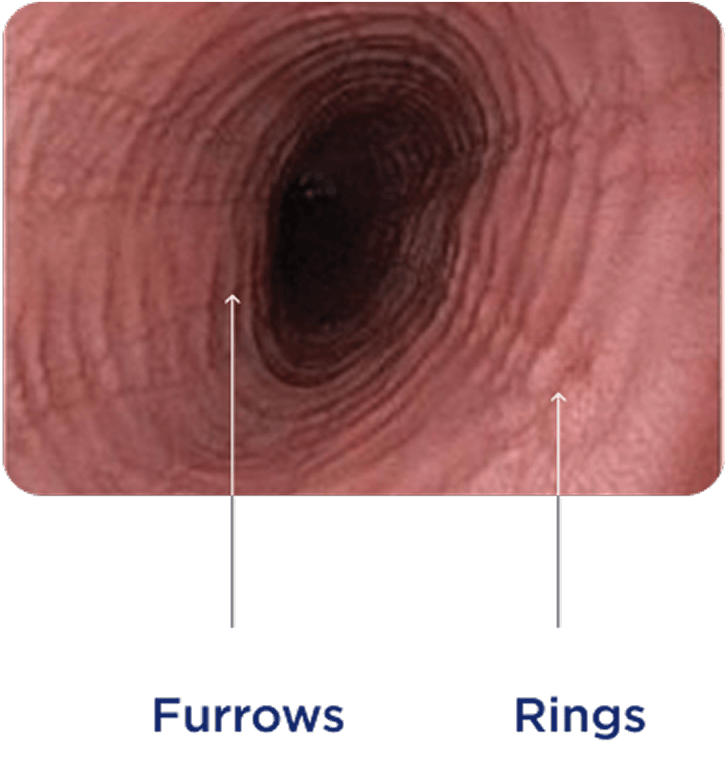
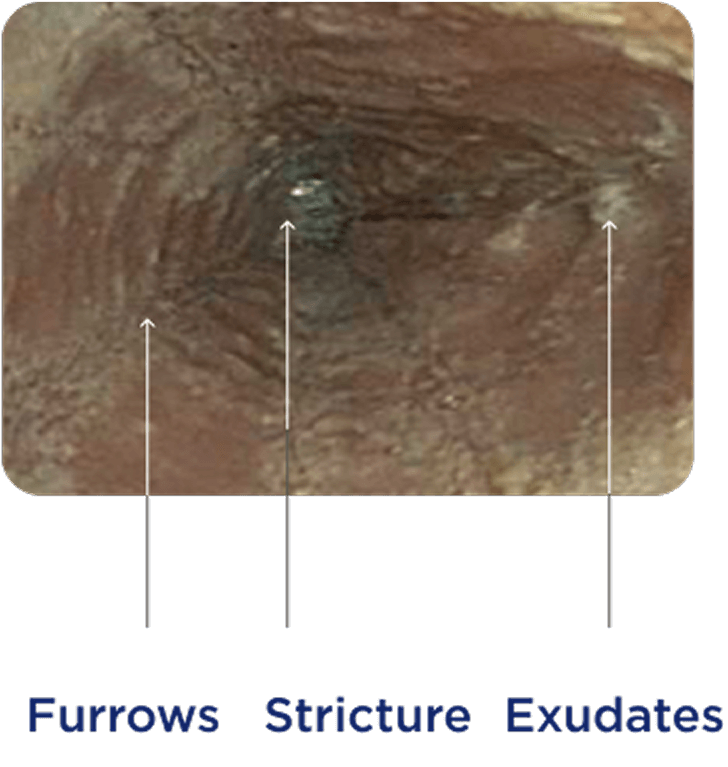
Endoscopic appearance can reveal inflammatory and fibrostenotic structural changes in the esophagus1,16,17
Endoscopic features can be used to help evaluate disease.
Endoscopic reference score (EREFS) assesses and grades the severity of 5 key esophageal features: edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and stricture.
The ACG guidelines and ASGE consensus paper recommend routinely using
EREFS when assessing EoE activity during endoscopy1,4
EoE requires long-term comprehensive management
Aim for initial treatment response across 3 key areas13
Assess treatments to confirm response and disease control
Many patients don’t respond adequately to common therapies like PPIs and TCS, or lose response later on.18,19

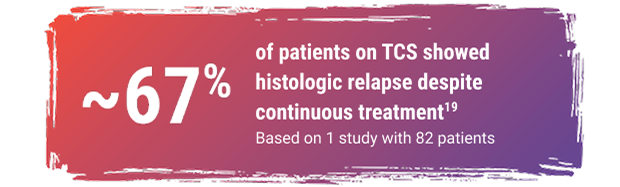
PPI, proton pump inhibitor; TCS, topical corticosteroid.
To maintain long-term control of EoE, ACG recommends:
![]()
Staying on a maintenance treatment
even after achieving initial response or a state of remission1,4
 Regular monitoring to ensure continued response
Regular monitoring to ensure continued response
and confirm there hasn’t been a recurrence of symptoms, inflammation,
or structural changes in the esophagus1,4
References: 1. Aceves SS, Alexander JA, Baron TH, et al. Endoscopic approach to eosinophilic esophagitis: American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Consensus Conference. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;96(4):576-592.e1. 2. Muir AB, Brown-Whitehorn T, Godwin B, Cianferoni A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: early diagnosis is the key. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:391-399. 3. Cheng E, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303(11):G1175-G1187. 4. Dellon E, Muir A, Katzka D, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2025;120(1)31-59. 5. Hiremath GS, Hameed F, Pacheco A, Olive A, Davis CM, Shulman RJ. Esophageal food impaction and eosinophilic esophagitis: a retrospective study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(11):3181-3193. 6. Attwood S, Lamb C. Eosinophilic oesophagitis and other non-reflux inflammatory conditions of the oesophagus: diagnostic imaging and best management. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterology. 2008;22(4):639-660. 7. Safroneeva E, Straumann A, Schoepfer AM. Latest insights on the relationship between symptoms and biologic findings in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28(1):35-45. 8. Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1230-1236.e2. 9. Gomez Torrijos E, Gonzalez-Mendiola R, Alvarado M, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: review and update. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018;5:247. doi:10.3389/fmed.2018.00247 10. de Rooij WE, Evertsz FB, Lei A, Bredenoord AJ. General well-being and coping strategies in adult eosinophilic esophagitis patients. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022;28(3):390-400. 11. Hirano I, Furuta GT. Approaches and challenges to management of pediatric and adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):840-851. 12. Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5(3):335-358. 13. Dellon ES, Gupta SK. A conceptual approach to understanding treatment response in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(11):2149-2160. 14. Gonsalves N, Pollicarpio-Nicolas M, Zhang Q, et al. Histopathologic variability and endoscopic correlates in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Sep;64(3):313-319. 15. Collins M. Histopathology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Dig Dis. 2014;32:(1-2)68-73. 16. Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(5):679-692. 17. Dellon ES, Hirano I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(suppl 4):1-16. 18. Lucendo AJ, Arias Á, Molina-Infante J. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor drugs for inducing clinical and histologic remission in patients with symptomatic esophageal eosinophilia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(1):13-22. 19. Greuter T, Godat A, Ringel A, et al. Effectiveness and safety of high- vs low-dose swallowed topical corticosteroids for maintenance treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: a multicenter observational study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(12):2514–2523.e2.