EoE IS A LIFELONG DISEASE THAT CAN HAVE SUBSTANTIAL IMPACT ON PATIENTS1,2
EoE is an inflammatory disease that is chronic and progressive3-6
EoE is a lifelong inflammatory disease that can take years to diagnose accurately and get under control2,4,7
![]()
It can take on average 5-8 years to diagnose EoE accurately7
![]()
Driven by underlying type 2 inflammation, EoE can progress to cause long-term damage, including esophageal remodeling and fibrosis4,5
~75% of patients with EoE have at least one coexisting type 2 inflammatory disease: allergic rhinitis, asthma, atopic dermatitis, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), and/or food allergies8-11
![]()
EoE requires a long-term management plan to help achieve and maintain control2,12
EoE significantly impacts patient and caregiver burden and quality of life1
Over the past two decades, the prevalence of EoE has rapidly increased13
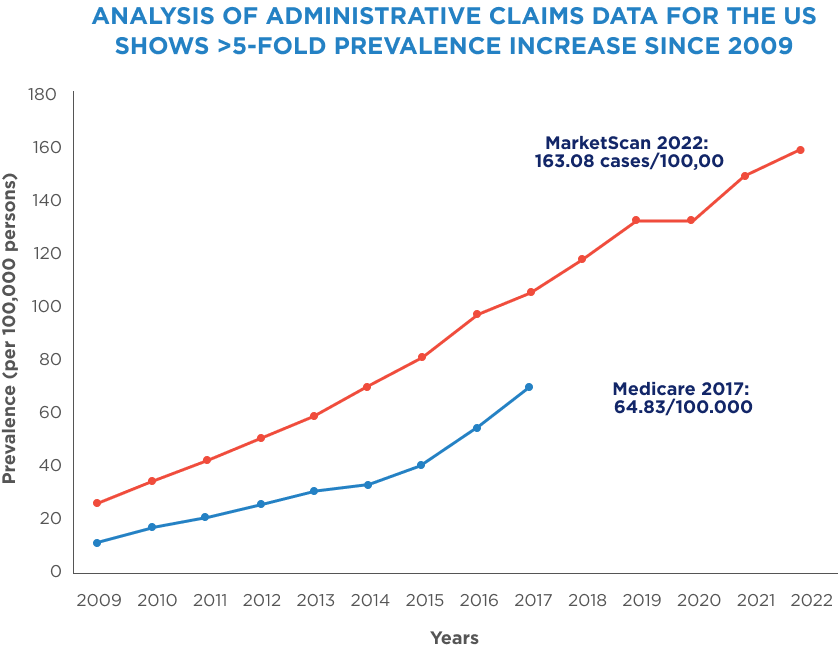
The prevalence of EoE has continually increased in the US and is estimated to impact approximately 1 in 700.13

EoE significantly impacts patient and caregiver burden and quality of life1

-
EoE patients may have dysphagia often causing chest pain and discomfort during meals14
- Social interactions involving food may cause stress, anxiety, and/or embarrassment, leading EoE patients to eat alone and avoid eating with others15
- Pediatric patients may struggle to maintain a healthy weight14


Persistent inflammation is
an unseen challenge
References: 1. Pokrzywinski RM, Harding G, Brooks A, Goodwin B, Williams J. Documenting the journey of patients with eosinophilic esophagitis and the impact of the disease on patients and their caregivers: a cross-sectional, qualitative research study. Adv Ther. 2020;37(10):4458-4478. 2. Aceves SS, Alexander JA, Baron TH, et al. Endoscopic approach to eosinophilic esophagitis: American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Consensus Conference. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;96(4):576-592.e1. 3. Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5(3):335-358. 4. Cheng E, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303(11):G1175-G1187. 5. Chehade M, Falk GW, Aceves S, et al. Examining the role of type 2 inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022;1(5):720-732. 6. Bredenoord AJ, Patel K, Schoepfer AM, et al. Disease burden and unmet need in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117(8)1231-1241.
7. Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1230-1236.e2. 8. van Rhijn BD, Bredenoord AJ. Management of eosinophilic esophagitis based on pathophysiological evidence. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(8):659-668. 9. Jyonouchi S, Brown-Whitehorn TA, Spergel JM. Association of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders with other atopic disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009;29(1):85-97. 10. Padia R, Curtin K, Peterson K, Orlandi RR, Alt J. Eosinophilic esophagitis strongly linked to chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(6):1279-1283. 11. Chehade M, Jones SM, Pesek RD, et al. Phenotypic characterization of eosinophilic esophagitis in a large multicenter patient population from the consortium for food allergy research. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2018;6(5):1534-1544.e5. 12. Dellon S. Muir A, Katzka D, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2025;120(1):31-59. 13. Thel H, Anderson C, Xue A, et al. Prevalence and costs of eosinophilic esophagitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Feb;23(2):272-280. 14. Muir AB, Brown-Whitehorn T, Godwin B, Cianferoni A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: early diagnosis is the key. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:391-399. 15. de Rooij WE, Evertsz FB, Lei A, Bredenoord AJ. General well-being and coping strategies in adult eosinophilic esophagitis patients. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022;28(3):390-400. 16. Mukkada V, Falk GW, Eichinger CS, King D, Todorova L, Shaheen NJ. Health-related quality of life and costs associated with eosinophilic esophagitis: a systematic review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(4):495-503.
