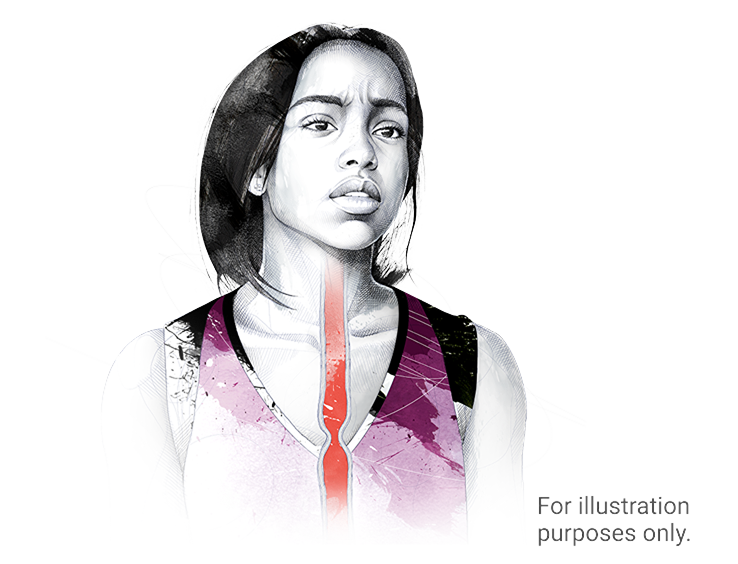

TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION IN EoE CAN PERSIST EVEN WHEN SYMPTOMS AREN’T THERE1
EoE, if left uncontrolled, often progresses from an inflammatory
to a fibrostenotic disease2-5
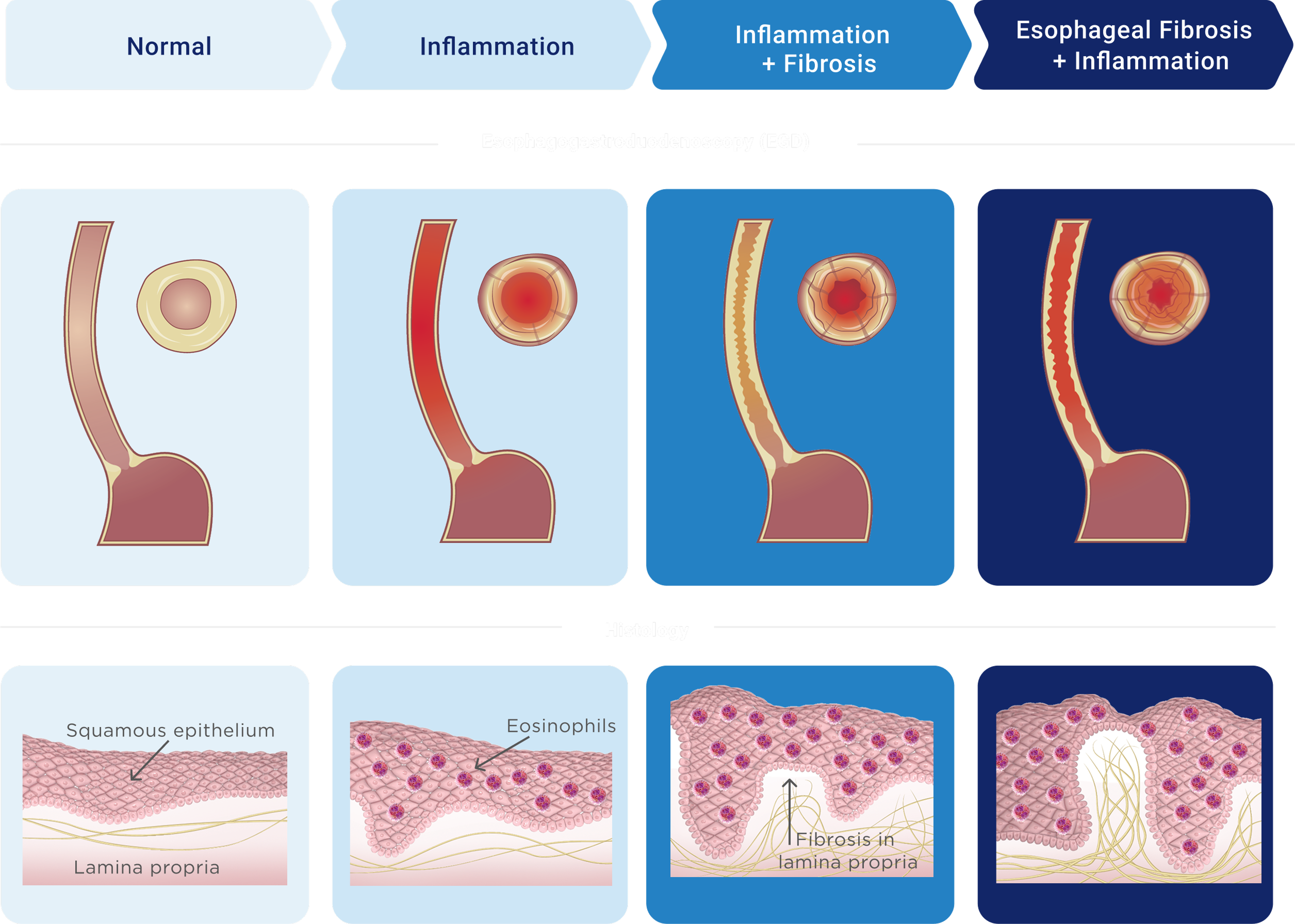



Disease progression may lead to serious long‑term complications and damage to the esophagus, including3,6:
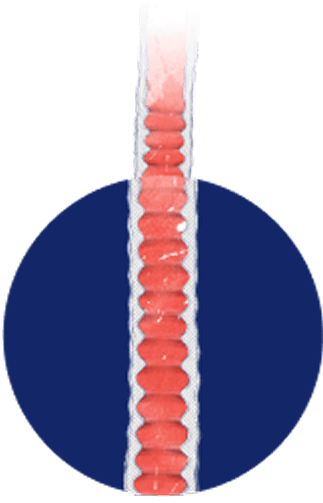
RINGS
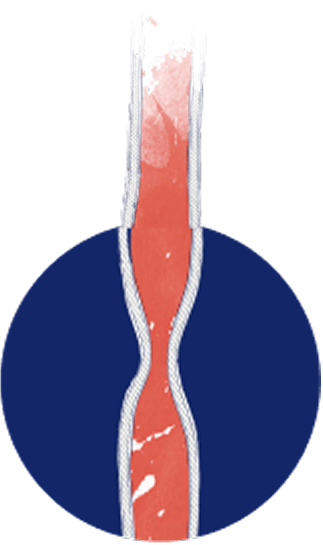
STRICTURES
(narrowings)
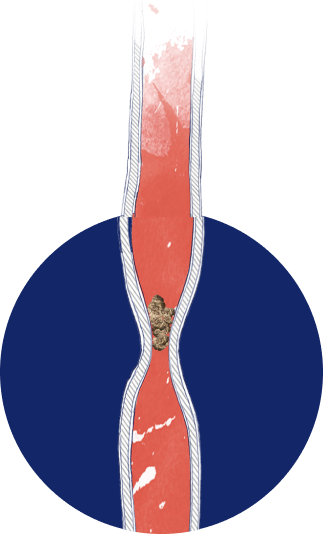
FOOD IMPACTION

To manage a chronic condition like EoE, you need a long‑term plan7
According to the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG), because EoE is chronic, disease activity almost always recurs when treatment is stopped.8,9

The impact of chronic and progressive EoE on patients’
lives reinforces the need for long-term disease control7
EoE is driven by type 2 inflammation2,11

TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION IS A MAJOR TYPE OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNE RESPONSE2,11,12
Defense against intracellular bacteria and viruses
Key cells and cytokines
Conditions associated with dysregulated type 1 inflammation: autoimmunity and certain metabolic disorders
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM)
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Celiac disease
Autoimmune gastritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD)
Defense against allergens and parasites
Key cells and cytokines
Conditions associated with dysregulated type 2 inflammation: allergic disorders
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Asthma
Atopic dermatitis
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Food allergy
Defense against extracellular bacteria and fungi
Key cells and cytokines

Conditions associated with dysregulated type 3 inflammation:
autoimmunity and certain chronic inflammatory disorders
Psoriasis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS)
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA)
Uveitis
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD)
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
When overactive, type 2 inflammation can result in diseases such as EoE,
atopic dermatitis, asthma, and other atopic conditions13-15
EoE PATHOGENESIS EXTENDS BEYOND EOSINOPHILS AND INVOLVES UNDERLYING TYPE 2 INFLAMMATION2
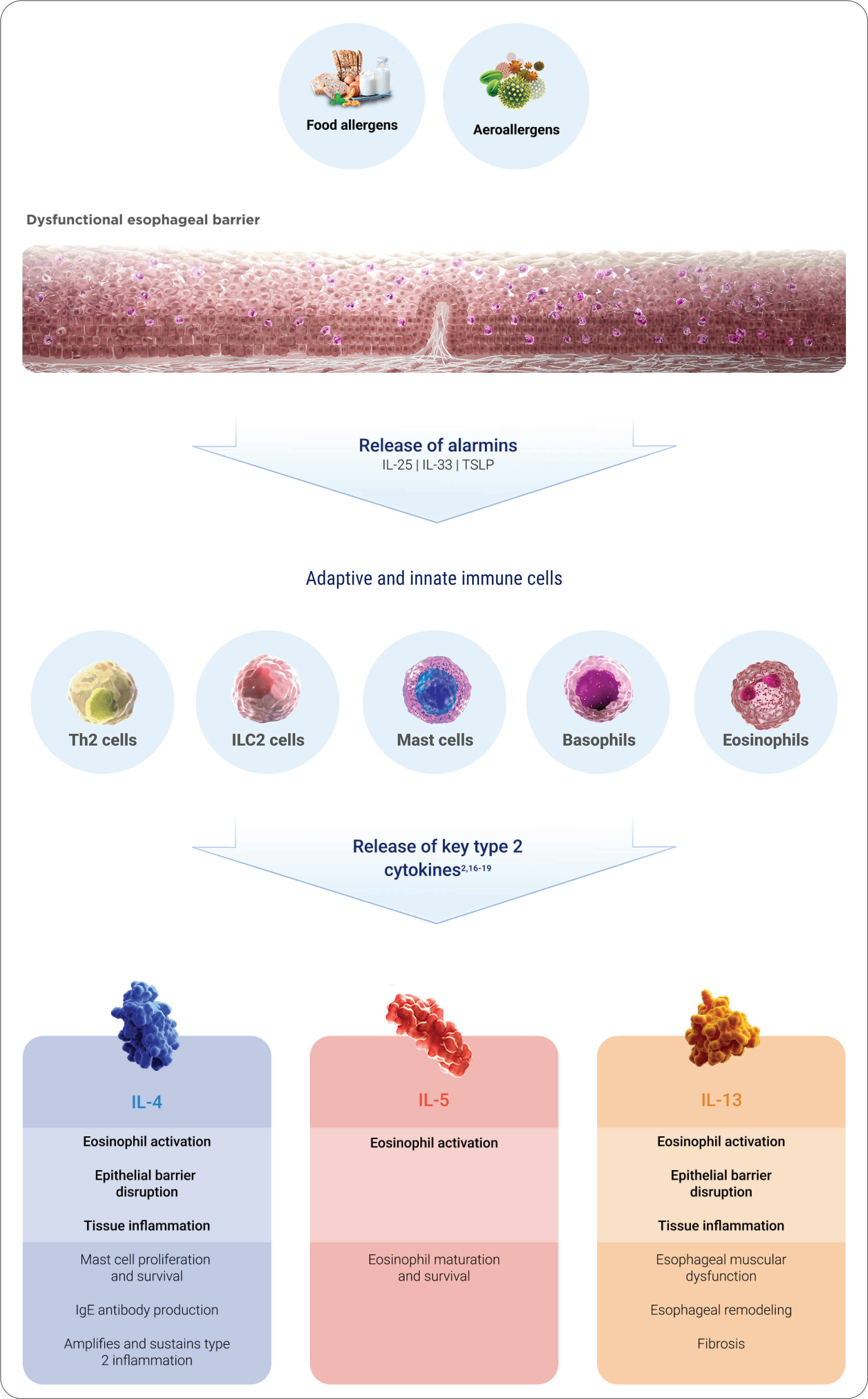
IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 are key mediators of type 2 inflammation, directly
impacting EoE symptoms, histology, and endoscopic appearance2
Learn more about the role of inflammation in EoE
A comprehensive management approach is required to treat underlying inflammation in EoE

A long-term management
plan can help achieve control7,8
References: 1. Safroneeva E, Straumann A, Schoepfer AM. Latest insights on the relationship between symptoms and biologic findings in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2018;28(1):35-45. 2. Chehade M, Falk GW, Aceves S, et al. Examining the role of type 2 inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022;1(5):720-732. 3. Cheng E, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Tissue remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303(11):G1175-G1187. 4. Dellon ES, Hirano I. Epidemiology and natural history of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(2):319-332. 5. Hirano I, Furuta GT. Approaches and challenges to management of pediatric and adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(4):840-851. 6. Muir AB, Brown-Whitehorn T, Godwin B, Cianferoni A. Eosinophilic esophagitis: early diagnosis is the key. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019;12:391-399. 7. Aceves SS, Alexander JA, Baron TH, et al. Endoscopic approach to eosinophilic esophagitis: American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Consensus Conference. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;96(4):576-592.e1. 8. Dellon S. Muir A, Katzka D, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and management of eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2025;120(1):31-59. 9. Bredenoord AJ, Patel K, Schoepfer AM, et al. Disease burden and unmet need in eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117(8):1231-1241. 10. Schoepfer AM, Safroneeva E, Bussmann C, et al. Delay in diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis increases risk for stricture formation in a time-dependent manner. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(6):1230-1236.e2. 11. Annunziato FA, Romagnani C, Romagnani S. The 3 major types of innate and adaptive cell-mediated effector immunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;135(3):626-635. 12. Gandhi NA, Bennett BL, Graham NMH, Pirozzi G, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(1):35-50. 13. van Rhijn BD, Bredenoord AJ. Management of eosinophilic esophagitis based on pathophysiological evidence. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(8):659-668. 14. Jyonouchi S, Brown-Whitehorn TA, Spergel JM. Association of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders with other atopic disorders. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009;29(1):85-97. 15. Padia R, Curtin K, Peterson K, Orlandi RR, Alt J. Eosinophilic esophagitis strongly linked to chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(6):1279-1283. 16. Underwood B, Troutman TD, Schwartz JT. Breaking down the complex pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023;130(1):28-39. 17. Sherrill JD, Kc K, Wu D, et al. Desmoglein-1 regulates esophageal epithelial barrier function and immune responses in eosinophilic esophagitis. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7(3):718-729. 18. O’Shea KM, Aceves SS, Dellon ES, et al. Pathophysiology of eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(2):333-345. 19. Leung J, Beukema KR, Shen AH. Allergic mechanisms of eosinophilic oesophagitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29(5):709-720.
